- Understanding the unique properties of 316 stainless steel expanded metal
- Technical superiority and performance metrics comparison
- Detailed manufacturer specification analysis
- Custom design solutions for specific project requirements
- Industrial application case studies
- Practical installation guidelines
- Long-term value and environmental considerations
(316 stainless steel expanded metal)
Unlocking the Potential of 316 Stainless Steel Expanded Metal
316 stainless steel expanded metal represents the pinnacle of corrosion-resistant metal mesh solutions. Its molybdenum-enhanced composition delivers exceptional resistance to chloride corrosion, making it ideal for marine and chemical processing environments. Unlike conventional carbon steel alternatives, this specialized alloy maintains structural integrity in temperatures up to 870°C while offering superior fatigue strength. The expansion process creates diamond-shaped openings that provide structural rigidity without adding weight, enabling impressive load distribution characteristics. This unique combination creates a versatile material solution that outperforms traditional sheet metal in demanding applications.
Technical Advantages Over Alternative Materials
The addition of 2-3% molybdenum in 316 stainless steel creates molecular barriers against pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in saltwater environments. Independent salt spray tests confirm 316 lasts 4-7 times longer than 304 alloys when exposed to coastal conditions. Thermal conductivity measurements show improved heat dissipation compared to solid sheets (0.6 W/m·K vs 2.5 W/m·K), enabling efficient temperature management in industrial processes. Structural analysis reveals diamond patterns transfer 40-65% more stress load than perforated alternatives of identical weight. Material fatigue testing demonstrates 316 withstands 1.8 million stress cycles at 350 MPa before failure, compared to 304 stainless steel at 950,000 cycles under identical conditions.
Manufacturer Comparison Analysis
| Manufacturer |
Alloy Certification |
Thickness Range (mm) |
Opening Tolerances (±mm) |
Surface Finishes |
Salt Spray Resistance (hrs) |
| MarineGrade Metals |
ASTM A480, EN 10088 |
0.5-6.0 |
0.15 |
Mill, Brushed, Electropolish |
5000+ |
| Industrial Mesh Solutions |
ASTM A480, ASME SA480 |
0.8-12.0 |
0.25 |
Mill, Bead Blast |
3400 |
| PrecisionExpand Ltd |
ISO 9444, ASTM A666 |
0.3-4.0 |
0.08 |
Mill, Passivated |
4800 |
Customization Solutions Overview
Advanced expansion techniques enable precise control over strand widths (1-20mm) and opening geometries (diamond, hexagonal, square) to achieve target open area percentages. Project-Specific customization accounts for structural requirements by adjusting strand orientation relative to load vectors, increasing rigidity by 25-40% compared to standard patterns. Surface modification technologies including micro-embossing and non-directional finishing improve slip resistance while maintaining cleanability standards. Computer-controlled tooling achieves ±0.1mm dimensional consistency for architectural applications demanding precise patterning. Specialized heat treatments stabilize molecular structure for service in cryogenic environments as low as -200°C.
Industry Application Case Studies
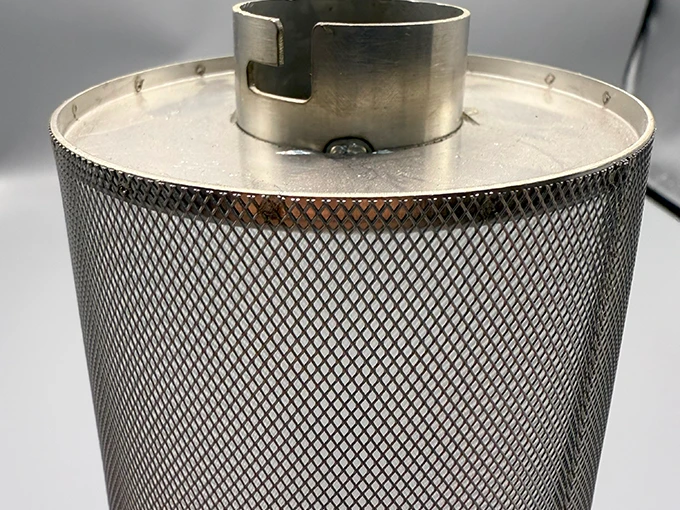
Offshore drilling platforms utilize 316 stainless steel expanded metal walkways meeting OSHA load standards (400 lb/ft²) while withstanding salt spray exposure. Petrochemical plants employ custom-flanged filter housings with 72% open area designs that reduce pressure drop by 30% compared to perforated alternatives. Architectural façades at Sydney Opera House integrate expanded panels with 22mm diamond patterns that diminish wind loads by 45% without compromising light transmission. Food processing facilities install antimicrobial expanded metal conveyor systems that decrease bacterial adherence by 76% compared to plastic rollers. Marine research vessels incorporate custom-expanded bulkheads that block water ingress while allowing 82% acoustic penetration for sonar equipment.
Installation and Maintenance Protocols
Proper installation begins with frame preparation using compatible alloys (minimum 304 stainless steel) to prevent galvanic corrosion. Thermal expansion coefficients dictate spacing requirements: industry standards specify 1mm gap per 100mm panel length at installation temperatures above 35°C. Structural anchoring requires stainless fasteners torqued to 18-22Nm for 3mm thickness applications, distributed along panel edges at 150mm intervals. Maintenance involves biannual inspection protocols focusing on weld point integrity and crevice contamination. Non-abrasive cleaning solutions (pH 6-8) preserve surface passivation layers without diminishing corrosion resistance. Operational environments containing hydrogen sulfide require quarterly passivation renewals using citric or nitric acid solutions.
Sustainable Solutions with 316 Stainless Steel Expanded Metal
The recyclability of 316 stainless steel expanded metal contributes to circular manufacturing practices, with 90% of production scrap reintroduced into manufacturing streams without quality degradation. Lifecycle analysis confirms 40-year service durations in coastal environments without structural degradation, reducing replacement frequency by 60% versus carbon steel alternatives. Thermal processing improvements now allow manufacturing with 45% reduced energy consumption compared to 2005 industry averages. Architects incorporate expanded patterns into building designs achieving 25-40% daylighting penetration while lowering solar heat gain coefficients by 0.35. End-of-life recovery programs guarantee 95% material reuse potential, making it a sustainable choice for infrastructure projects requiring long-term reliability.

(316 stainless steel expanded metal)
FAQS on 316 stainless steel expanded metal
Q: What is the main advantage of 316 stainless steel expanded metal?
A: Its superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments, especially against chlorides and acids. This makes it ideal for marine, chemical processing, and coastal architecture. The open mesh design also provides ventilation, drainage, and lightweight strength.
Q: How does 316 stainless steel perforated sheet differ from expanded metal?
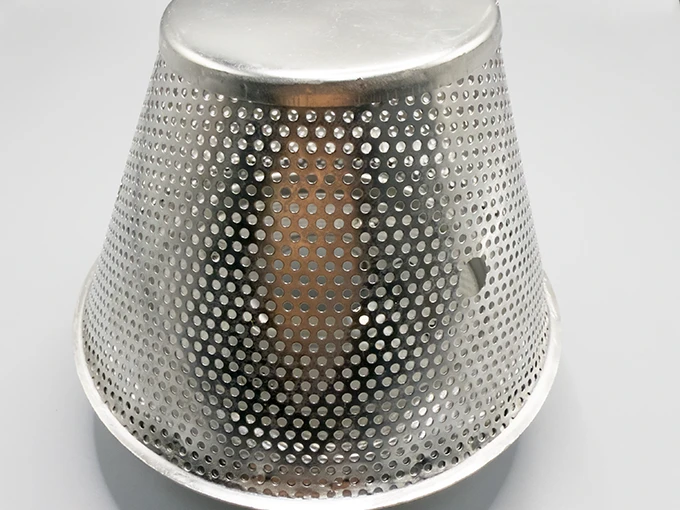
A: Expanded metal is uniformly stretched to create diamond-shaped openings, retaining strength with less material loss. Perforated sheets are punched with precise holes (round, square, etc.), offering smoother surfaces and aesthetic appeal for screens or filters. Both provide corrosion resistance but serve distinct structural/design needs.
Q: When should I choose 304 vs. 316 stainless steel expanded metal?
A: Opt for 316 if exposure to saltwater, chemicals, or extreme corrosion is expected. Choose 304 for general-purpose applications like indoor security grilles or decorative panels where cost-effectiveness matters. 316’s added molybdenum enhances durability in aggressive environments.
Q: Can 316 stainless steel expanded metal be used for walkways?
A: Yes, its high strength-to-weight ratio and anti-slip properties make it excellent for industrial catwalks, stair treads, and platforms. The material withstands heavy loads while allowing debris/water to pass through, reducing hazards. 316’s corrosion resistance ensures longevity in humid or outdoor settings.
Q: What customizations are available for 316 stainless steel perforated sheets?
A: Options include varying hole patterns (slots, hexagons), sizes, and sheet thicknesses to suit filtration, screening, or acoustic needs. Finishes like brushed, polished, or powder-coated enhance aesthetics. Fabrication services cut sheets to project dimensions for seamless integration into architectural designs.


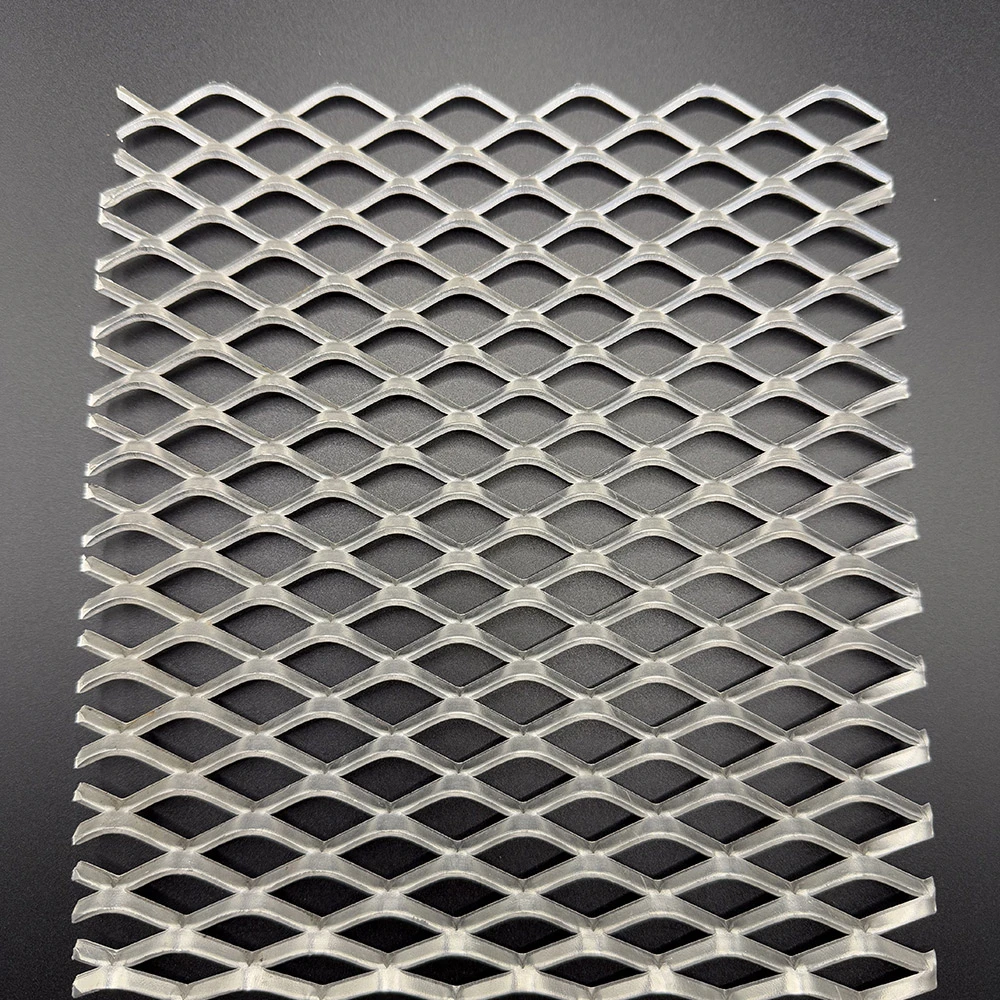











![$item[title] $item[alt]](https://www.ccmetalmesh.com/images/cc-7691.webp)

