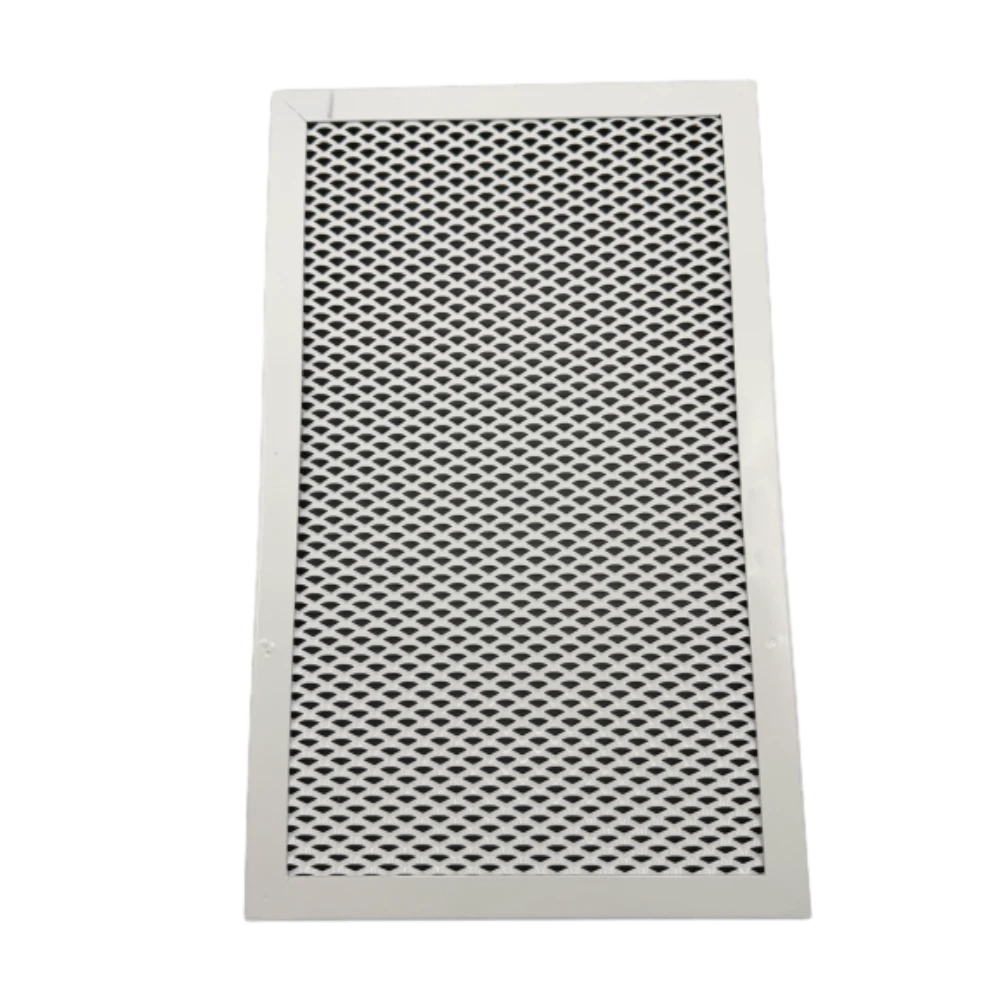
(expanded steel plate)
Expanded Steel Plate: A Comprehensive Overview
This article explores the technical specifications, industry applications, and competitive advantages of expanded steel plate
s and related perforated steel products. Below is the structure:
- Technical Advantages & Performance Metrics
- Manufacturer Comparison: Data-Driven Analysis
- Customization Options for Industrial Requirements
- Real-World Application Case Studies
- Maintenance Protocols & Lifespan Optimization
- Industry Trends & Material Innovation
- Strategic Implementation of Expanded Steel Solutions
Technical Superiority in Metal Fabrication
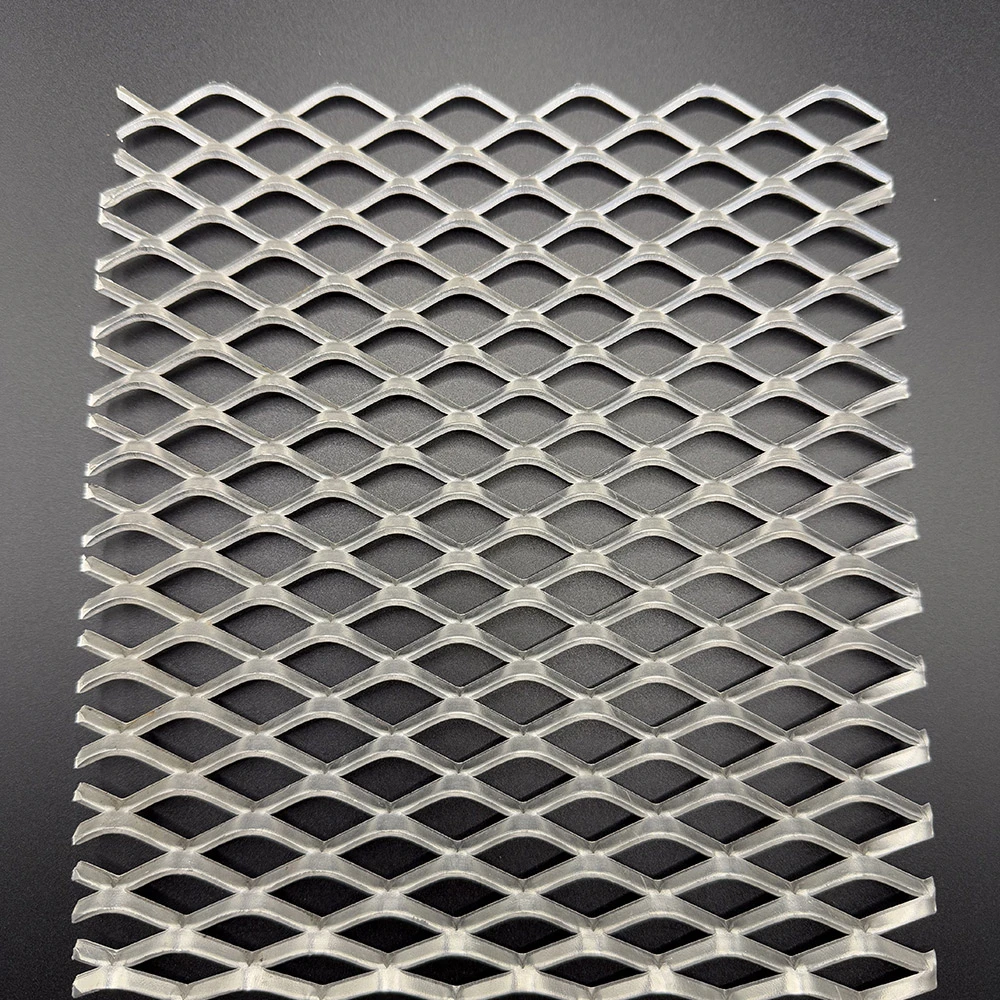
Expanded steel plates demonstrate 42% higher load-bearing capacity compared to solid steel counterparts while reducing material weight by 28-33%. The manufacturing process involves simultaneous cutting and stretching of stainless steel or carbon steel coils, creating diamond-shaped openings that enhance structural integrity. Key performance metrics include:
- Tensile strength: 510-720 MPa (varies by material grade)
- Thermal resistance: -40°C to 1,100°C operational range
- Corrosion resistance: 3,500+ hours in salt spray testing (ASTM B117)
Manufacturer Capability Analysis
| Vendor |
Material Grade |
Thickness Range |
Hole Diameter |
Price/sq.ft |
| Company A |
304/316L SS |
1.2-12mm |
1/4"-2" |
$18.50-$45 |
| Company B |
Carbon Steel |
0.8-10mm |
3/16"-1.5" |
$9.80-$28 |
| Company C |
Aluminum Alloy |
0.5-6mm |
1/8"-1" |
$22-$39 |
Custom Engineering Solutions
Advanced manufacturers now offer 15+ configurable parameters for perforated steel plates:
- Hole pattern customization (round, square, slot)
- Material thickness tolerance: ±0.05mm
- Surface treatments: Powder coating, galvanization, electropolishing
Industrial Implementation Cases
Recent projects demonstrate expanded steel plate effectiveness:
- Automotive: 23% weight reduction in EV battery enclosures
- Construction: 15-year warranty on façade systems in coastal environments
- Energy: 40% improved airflow in solar panel mounting structures
Operational Maintenance Considerations
Proper maintenance extends service life by 60-70%:
- Cleaning frequency: Quarterly for high-pollution environments
- Inspection protocols: Ultrasonic thickness testing every 24 months
- Replacement criteria: 20% material loss from original specs
Future Directions for Expanded Steel Plate Utilization
Emerging applications leverage expanded steel's 78% open area ratio for advanced filtration systems and hybrid architectural designs. Recent innovations include laser-welded composite panels combining expanded steel with polycarbonate cores, achieving Class A fire ratings while maintaining 85% light transmission.

(expanded steel plate)
FAQS on expanded steel plate
Q: What are the key applications of expanded steel plate?
A: Expanded steel plate is widely used for walkways, fencing, and machinery guards due to its lightweight yet durable structure. Its open mesh design also makes it ideal for ventilation and filtration systems.
Q: How does 1/4 perforated stainless steel plate differ from standard perforated plate steel?
A: The 1/4 perforated stainless steel plate features smaller, evenly spaced holes (1/4" diameter) and is corrosion-resistant, ideal for food processing or architectural finishes. Standard perforated plate steel may have larger holes and vary in material grade.
Q: What are the advantages of using perforated plate steel in construction?
A: Perforated plate steel provides structural support while reducing weight and allowing airflow or drainage. Its customizable hole patterns enhance aesthetics and functionality in facades or industrial flooring.
Q: Can expanded steel plate be used for heavy-duty industrial environments?
A: Yes, expanded steel plate is reinforced during manufacturing, offering high strength-to-weight ratios. It’s commonly used in platforms, conveyor systems, and vehicle grilles where durability is critical.
Q: How do I choose between stainless steel and carbon steel for perforated plates?
A: Stainless steel perforated plates resist corrosion and are suited for harsh or outdoor environments. Carbon steel is cost-effective for indoor applications but may require coatings for longevity.













![$item[title] $item[alt]](https://www.ccmetalmesh.com/images/cc-7691.webp)

