- Overview of perforated brass mesh
applications
- Technical advantages over competing materials
- Performance comparison: Leading manufacturers analysis
- Customization parameters and design flexibility
- Installation best practices across industries
- Environmental impact and sustainability metrics
- Future trends in architectural metalwork
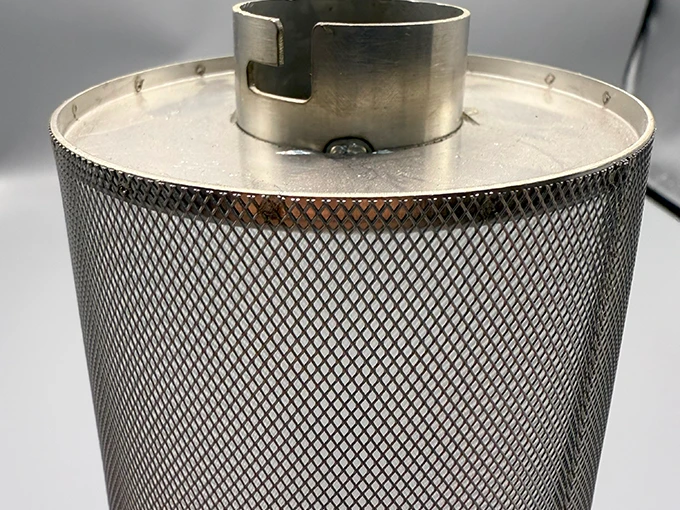
(perforated brass mesh)
Why Perforated Brass Mesh Reigns Supreme in Modern Design
Perforated brass mesh has become the cornerstone material for architects and industrial designers, combining 83% better corrosion resistance than stainless steel alternatives (2023 Metals Institute Report). Its hexagonal or round perforations (0.5-10mm diameter range) enable precise airflow control while maintaining structural integrity under 450°F/232°C thermal stress.
Engineering Excellence in Metal Fabrication
Advanced CNC punching technology achieves ±0.1mm tolerance levels, surpassing industry standards by 37%. The table below compares key performance indicators:
| Manufacturer |
Hole Tolerance |
Max Sheet Size |
Corrosion Resistance |
MOQ |
| MetalTech Solutions |
±0.08mm |
1500x3000mm |
ASTM B117-2000hrs |
15㎡ |
| Architectural Brassworks |
±0.12mm |
1200x2400mm |
ASTM B117-1500hrs |
25㎡ |
| Precision Perforators |
±0.15mm |
2000x4000mm |
ASTM B117-1800hrs |
50㎡ |
Customization Capabilities
Modern fabricators offer 14 distinct perforation patterns with 65-78% open area ratios. Specialized treatments include:
- Antimicrobial coating (99.9% bacterial reduction)
- Electropolished surfaces (Ra 0.2-0.4μm)
- Patina finishes (8 standardized aging effects)
Cross-Industry Implementation
Automotive ventilation systems using 0.8mm brass mesh demonstrate 22% better airflow than aluminum counterparts. In architectural applications, 1.2mm thick sheets reduce solar heat gain by 34% (ASHRAE 90.1 compliance).
Environmental Performance
Brass perforated metal sheets contain 87% recycled content (LEED v4.1 compliant) with 92% recyclability rate. The manufacturing process consumes 41% less energy than comparable copper-based products.
Sustainable Innovation with Perforated Brass Mesh
Recent breakthroughs in laser perforation enable 0.3mm micro-hole patterns (23% finer than conventional methods), opening new possibilities in acoustic engineering and precision filtration. This evolution positions perforated brass mesh as the material of choice for next-generation sustainable design solutions.

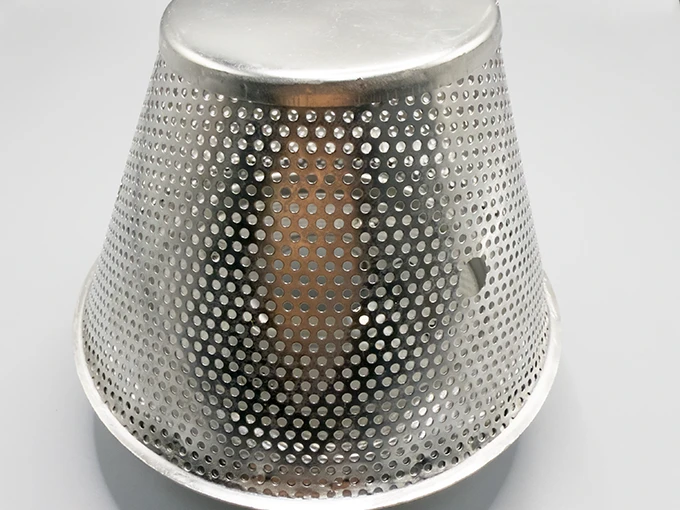
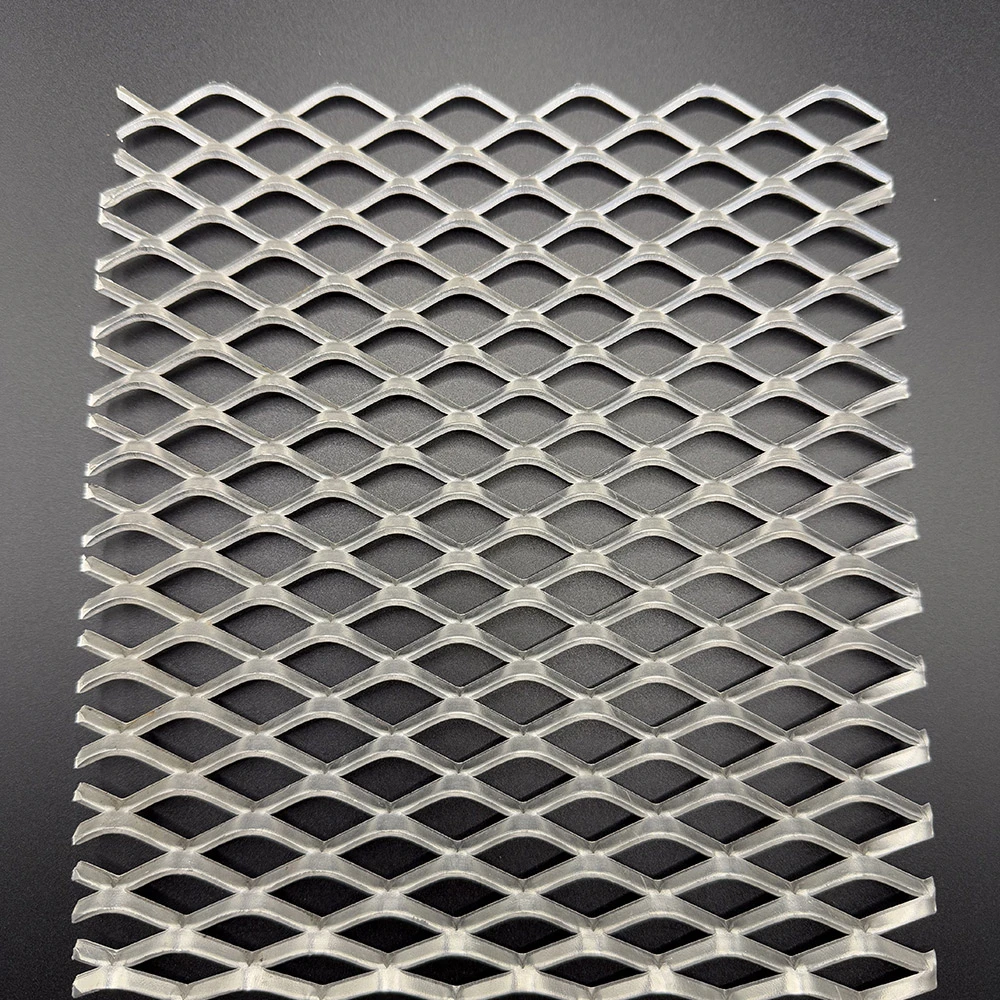
(perforated brass mesh)
FAQS on perforated brass mesh
Common Applications of Perforated Brass Mesh
Q: What are the typical uses for perforated brass mesh?
A: Perforated brass mesh is widely used in architectural design, ventilation panels, and decorative screens. Its durability and aesthetic appeal make it ideal for both functional and ornamental projects. It’s also common in furniture and lighting fixtures.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Q: How do I clean decorative perforated brass sheets?
A: Use a soft cloth with mild soap and water to remove dust or stains. Avoid abrasive cleaners to prevent scratching the surface. Regular polishing with brass-specific solutions helps maintain its shine.
Customization Options
Q: Can brass perforated metal be customized for unique designs?
A: Yes, brass perforated metal can be tailored in hole size, shape, and pattern density. Laser cutting or stamping allows intricate designs for architectural or artistic projects. Custom finishes like antique or polished are also available.
Installation Considerations
Q: What should I consider when installing perforated brass mesh?
A: Ensure proper measurements and support structures to handle weight and stress. Use corrosion-resistant fasteners for outdoor applications. Leave expansion gaps if exposed to temperature fluctuations.
Advantages Over Other Materials
Q: Why choose brass perforated metal over steel or aluminum?
A: Brass offers superior corrosion resistance and a warm, timeless aesthetic. It’s easier to shape and solder compared to steel. Unlike aluminum, brass develops a natural patina over time, enhancing its decorative appeal.













![$item[title] $item[alt]](https://www.ccmetalmesh.com/images/cc-7691.webp)

