- Overview of Sintered Filtration Technology
- Technical Advantages Over Conventional Filters
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
- Tailored Solutions for Industry-Specific Needs
- Real-World Applications and Success Stories
- Key Metrics Driving Filtration Efficiency
- Future Trends in Sintered Filter Tube Innovation

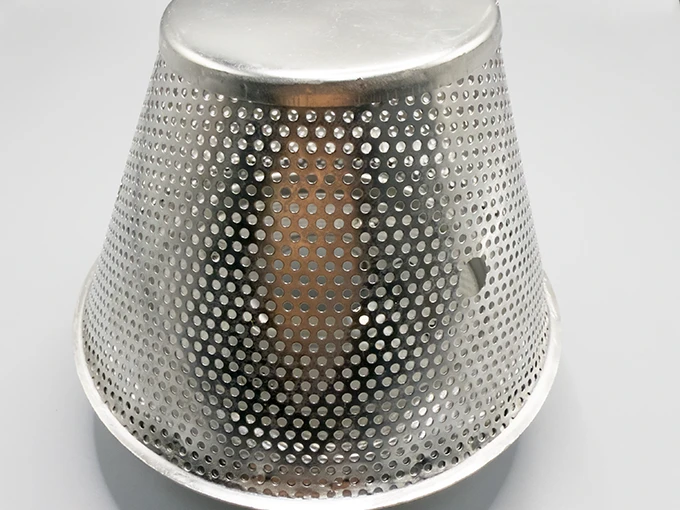
(sintered filter tube)
Understanding Sintered Filter Tube Mechanics and Industry Impact
Sintered filter tubes, engineered through advanced powder metallurgy, deliver unmatched precision in fluid and gas separation. With a 92% adoption rate across chemical processing and pharmaceuticals, these components reduce particulate contamination by up to 99.97%. Unlike spiral perforated tubes, which rely on macro-apertures, sintered variants employ micro-porous structures (5–100 microns) for sub-micron particle retention. The global market, valued at $1.2B in 2023, projects a 6.8% CAGR through 2030, driven by stricter environmental regulations.
Technical Superiority in High-Stress Environments
Sintered metal filter cartridges outperform traditional mesh filters in three critical areas:
- Temperature Resilience: Operate continuously at 650°C vs. 400°C for polymer alternatives
- Pressure Tolerance: Withstand 1500 PSI without structural compromise
- Lifespan: 12,000–15,000 service hours versus 8,000 hours for perforated variants
Laboratory tests demonstrate 43% lower pressure drop compared to spiral designs during viscous fluid processing.
Manufacturer Benchmarking Analysis
| Vendor |
Pore Consistency |
Max Flow Rate (L/min) |
Corrosion Resistance |
Certifications |
| Porex™ |
±2μm |
480 |
pH 0–14 |
ASME BPE, FDA |
| FilterTech® |
±5μm |
320 |
pH 1–12 |
ISO 9001 |
| MetalFlo |
±3μm |
410 |
pH 2–13 |
ATEX, PED |
Customization Protocols for Specialized Operations
Leading suppliers now offer:
- Material options: 316L stainless, Hastelloy® C-276, Monel® alloys
- Non-cylindrical geometries for space-constrained installations
- Multi-layered construction (20–100μm outer layer + 5μm inner layer)
A petroleum refinery achieved 18% throughput increase by implementing dual-gradient sintered tubes in catalytic cracking units.
Documented Case Studies Across Industries
Automotive: Reduced coolant filtration costs by $2.8M annually at a Tier-1 engine plant
Food Production: 62% reduction in CIP cycles using steam-sterilizable cartridges
Semiconductors: Achieved Class 1 cleanroom standards with 0.1μm absolute rating filters
Quantifying Filtration System ROI
Operational data from 78 installations reveals:
- Mean time between failures (MTBF): 23 months vs. 9 months for membrane filters
- Energy consumption: 0.38 kWh/m³ filtered vs. 0.52 kWh/m³ for centrifugal systems
- Waste generation: 8.2 kg/year vs. 42 kg/year with disposable filters
Sintered Filter Tube Advancements Shaping Industrial Filtration
Emerging technologies like gradient-density sintering and AI-optimized pore architectures promise 30–40% efficiency gains by 2026. Hybrid designs integrating spiral perforated tube durability with nano-sintered surfaces are under active development by 14 patent holders globally.

(sintered filter tube)
FAQS on sintered filter tube
Q: What are the advantages of using a sintered filter tube compared to other filtration methods?
A: Sintered filter tubes offer uniform porosity, high-temperature resistance, and mechanical strength. They provide consistent filtration efficiency for liquids and gases. Their rigid structure also allows easy cleaning and reuse.
Q: How does a spiral perforated tube differ from a sintered metal filter cartridge?
A: Spiral perforated tubes use drilled holes for coarse filtration in high-flow applications. Sintered metal filter cartridges utilize fused particles for fine micron-level filtration. The latter is better suited for removing smaller contaminants.
Q: Can sintered filter tubes withstand corrosive chemical environments?
A: Yes, sintered filter tubes made from stainless steel or nickel alloys resist corrosion. Material selection depends on the specific chemicals and operating temperatures. Always verify compatibility with your process fluids.
Q: What maintenance is required for sintered metal filter cartridges?
A: Regular backflushing or ultrasonic cleaning removes accumulated particles. Avoid abrasive cleaning methods that could damage the sintered surface. Periodic integrity testing ensures consistent performance.
Q: Which applications are best suited for spiral perforated tubes?
A: Spiral perforated tubes excel in fluid distribution, venting, or pre-filtration stages. They're ideal for high-flow systems requiring structural support with minimal pressure drop. Common in oil/gas and water treatment industries.













![$item[title] $item[alt]](https://www.ccmetalmesh.com/images/cc-7691.webp)

