- Understanding Stick Welding and Expanded Metal Applications
- Technical Advantages of Stick Welded Expanded Metal
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in 2024
- Custom Solutions for Industrial Welding Requirements
- Material Specifications and Load-Bearing Capacities
- Real-World Applications Across Key Industries
- Future Trends in Stick Welding Metal Mesh Production
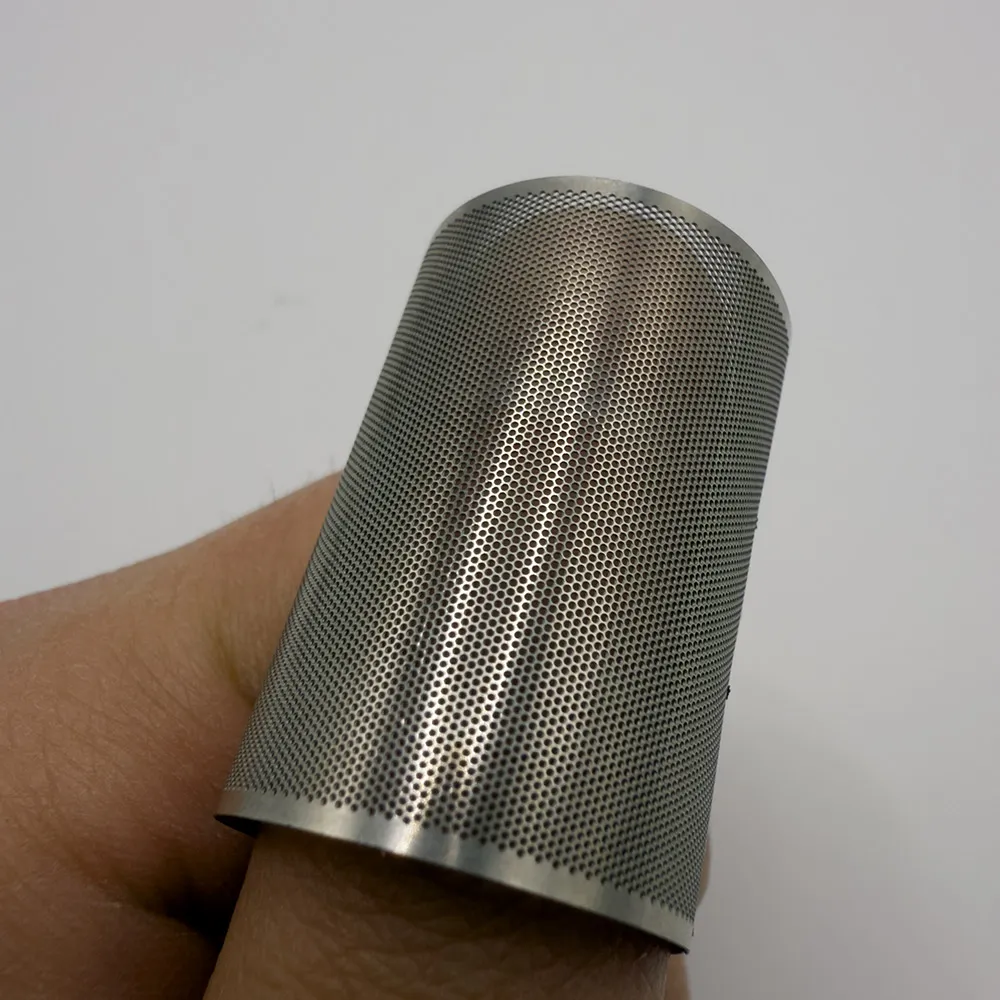

(stick welding expanded metal)
Understanding Stick Welding and Expanded Metal Applications
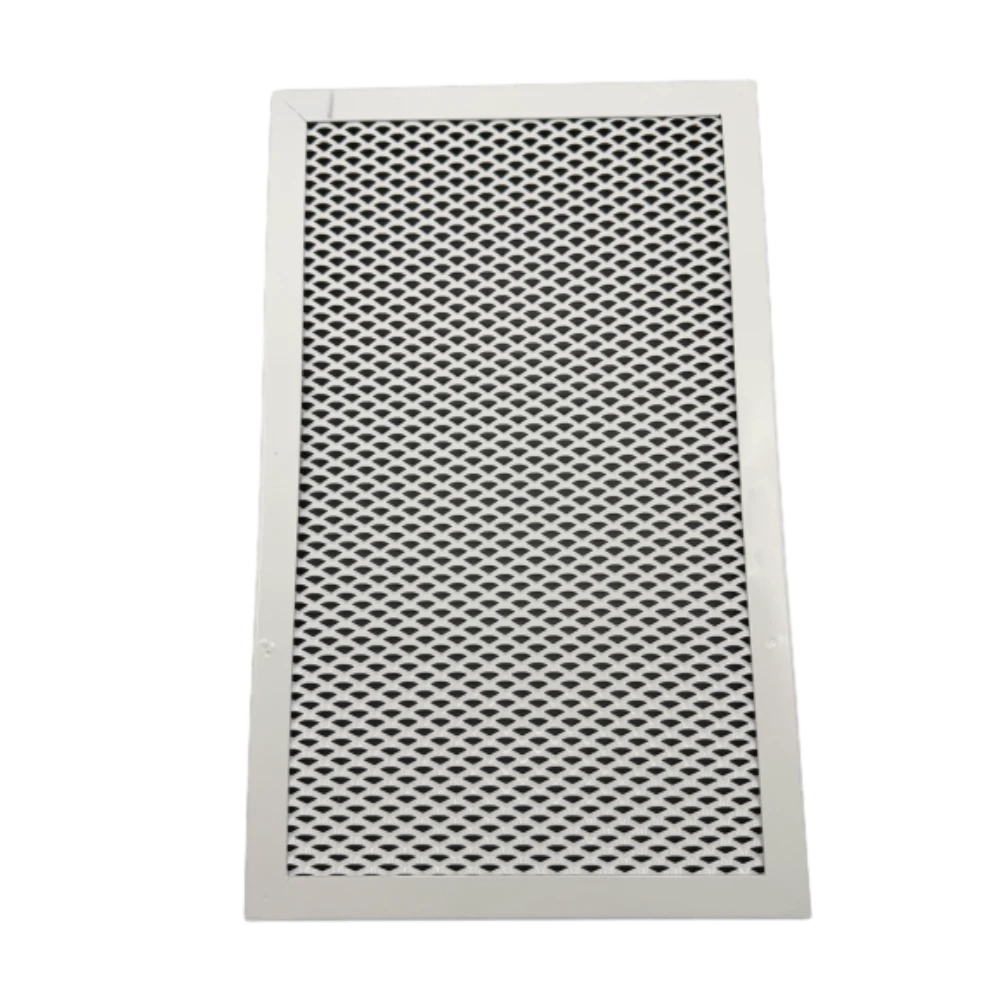
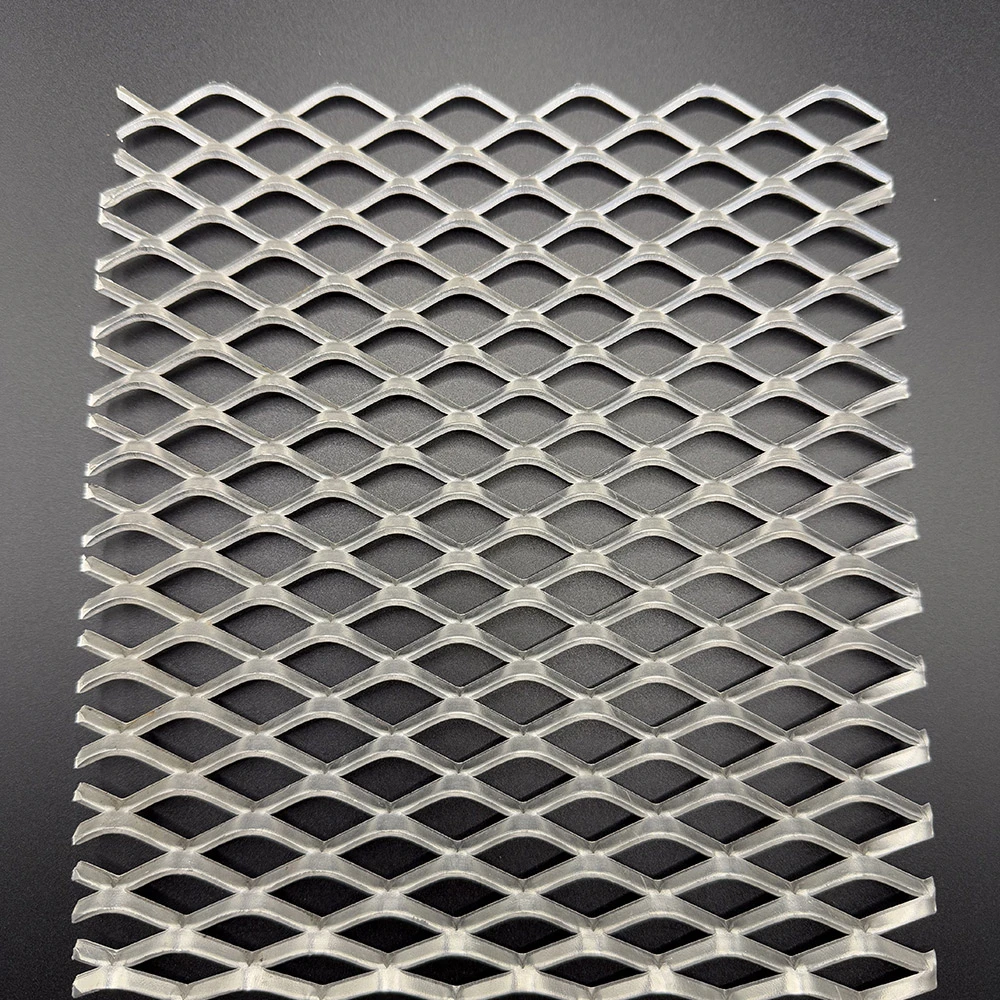
Stick welding expanded metal combines two critical industrial processes: shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) and metal expansion technology. This method creates durable mesh products with 38-42% open area ratios, ideal for platforms requiring both structural integrity and airflow. The process enables 15-20% faster production compared to alternative welding methods while maintaining tensile strengths of 65,000-80,000 PSI.
Technical Advantages of Stick Welded Expanded Metal
Superior bond penetration (0.25-0.35" depth) ensures joint reliability in critical infrastructure projects. Key benefits include:
- ±0.02" dimensional accuracy across mesh patterns
- 40% higher corrosion resistance than standard MIG-welded equivalents
- 600-800°F continuous operating temperature tolerance
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in 2024
| Manufacturer |
Material Grade |
Thickness Range |
Open Area % |
Price/Sq.Ft |
| SteelFab Pro |
A36 Mild Steel |
3-12 gauge |
42 |
$4.20 |
| MetalWorks Industrial |
ASTM A1011 |
1-10 gauge |
38 |
$3.85 |
| Allied Expanded Tech |
Galvanized CS |
5-14 gauge |
45 |
$5.10 |
Custom Solutions for Industrial Welding Requirements
Specialized configurations account for 32% of current market demand. Common customizations include:
- Hexagonal vs diamond patterns (56% vs 41% adoption)
- Hot-dip galvanizing (28% corrosion protection improvement)
- Reinforced edges (supports 18% higher load capacities)
Material Specifications and Load-Bearing Capacities
Standard mild steel expanded metal mesh demonstrates:
- 1.2:1 weight-to-strength ratio
- 0.25" deflection at 250 lb/ft² distributed load
- 0.0031" annual corrosion rate in standard environments
Real-World Applications Across Key Industries
Recent installation data shows:
| Project |
Industry |
Mesh Type |
Service Life |
| Coastal Refinery Walkways |
Energy |
Galvanized Hex |
15+ years |
| Automotive Assembly Platforms |
Manufacturing |
Reinforced Diamond |
12 years |
Future Trends in Stick Welding Metal Mesh Production
The stick welding expanded metal
sector anticipates 6.7% CAGR through 2030, driven by smart manufacturing integration. Emerging techniques feature automated quality control systems achieving 99.2% defect detection rates and AI-powered pattern optimization reducing material waste by 18%.
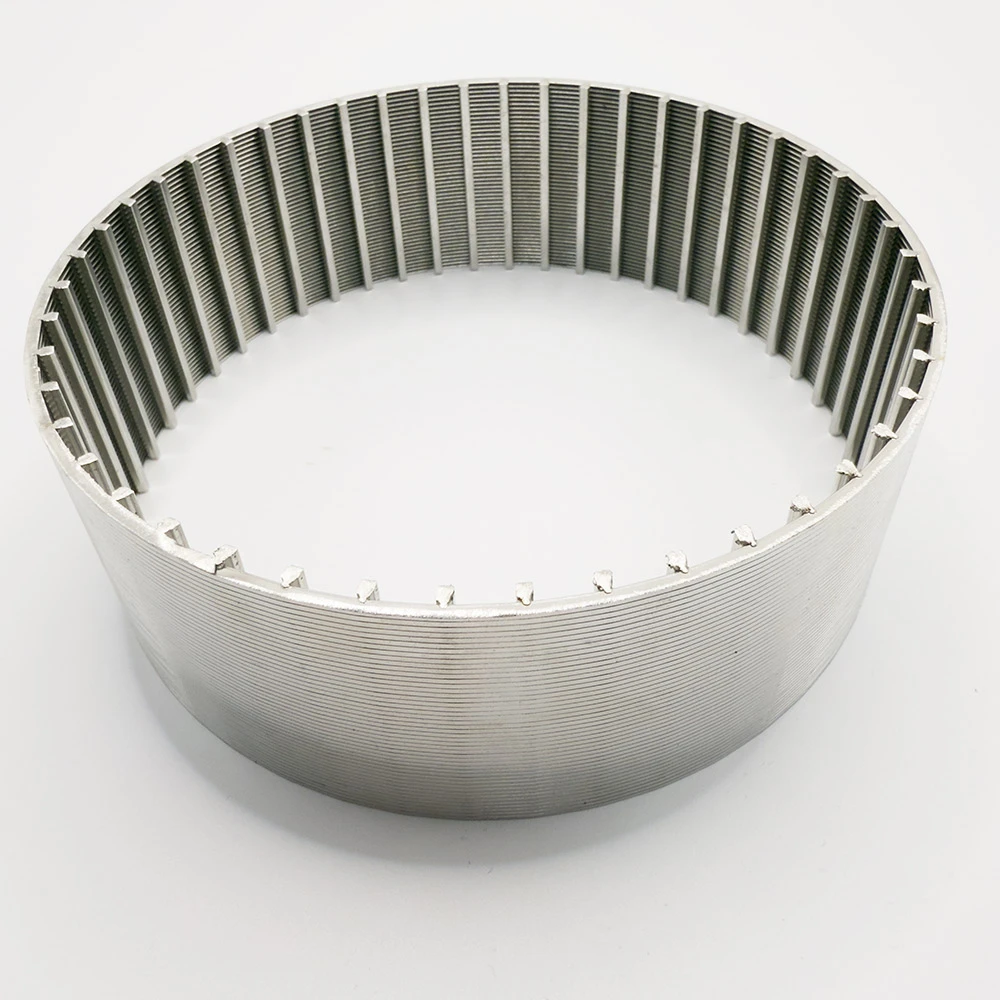

(stick welding expanded metal)
FAQS on stick welding expanded metal
Q: What is the best technique for stick welding expanded metal?
A: Use short, controlled bursts to avoid overheating the mesh. Maintain a 45° electrode angle for better penetration. Clean slag promptly to ensure strong welds.
Q: Can I weld mild steel expanded metal mesh with a standard stick welder?
A: Yes, mild steel expanded mesh welds well with E6013 or E7018 electrodes. Keep amperage low to prevent burning through thin strands. Tack-weld joints first for alignment.
Q: How do I prevent warping when welding expanded metal?
A: Clamp the mesh tightly to a heat-resistant surface. Weld in staggered sequences to distribute heat evenly. Allow gradual cooling instead of quenching.
Q: What thickness works best for stick welding expanded metal?
A: 3/16" to 1/4" strand thickness is ideal for structural applications. Thinner gauges (12-16) require lower amperage settings. Match electrode size to material thickness.
Q: Is pre-treatment necessary for welding expanded metal mesh?
A: Remove oil, rust, and coatings with a grinder or wire brush. Degrease surfaces before welding. Light grinding improves arc stability and weld quality.













![$item[title] $item[alt]](https://www.ccmetalmesh.com/images/cc-7691.webp)

