- Fundamentals of filtration mesh technology
- Material science behind effective water filtration
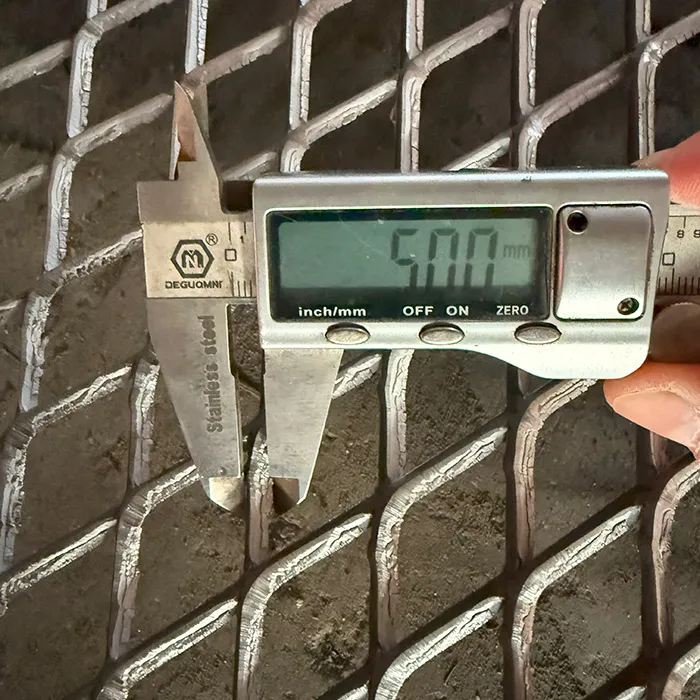
- Weaving patterns and precision manufacturing
- Performance comparison of leading mesh producers
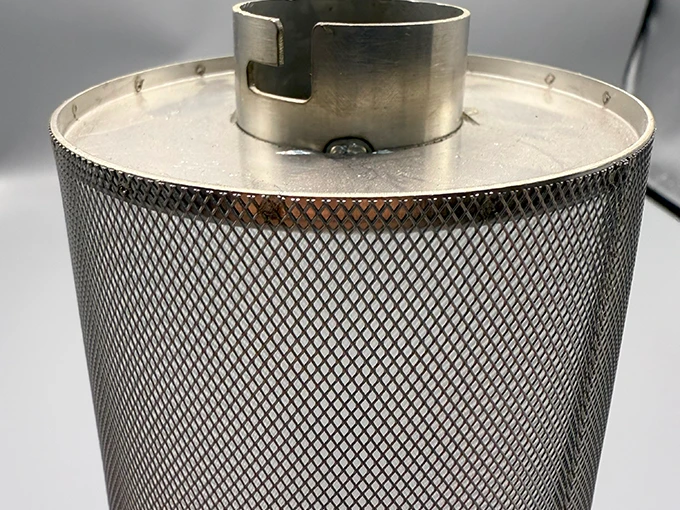
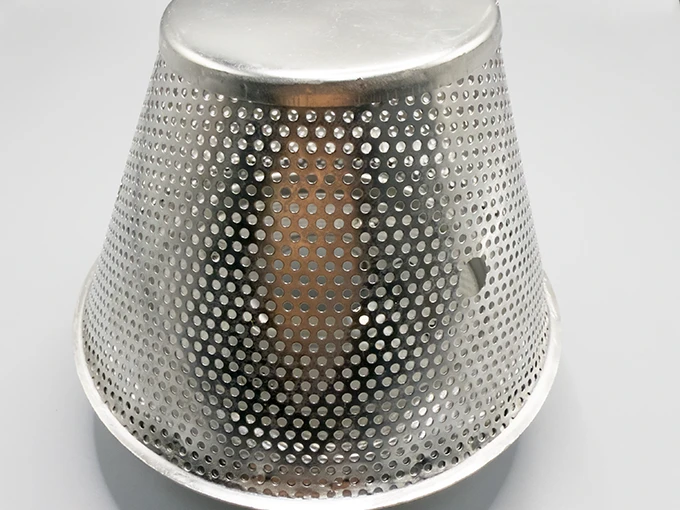
- Custom engineering solutions for specific applications
- Industrial implementation case studies
- Emerging advancements in micro-filtration

(water filtration mesh)
Understanding Water Filtration Mesh Fundamentals
Modern water treatment systems rely on filtration mesh as their primary defense against contaminants. These precision-engineered barriers remove particles ranging from 1 micron to several millimeters through physical sieving. Industries from pharmaceuticals to food processing depend on consistent mesh performance where a 5% variation in aperture size can reduce filtration efficiency by up to 40%. Unlike paper filters, woven metal or polymer meshes offer reusable solutions capable of processing over 500,000 liters before replacement. The hydraulic performance remains stable with less than 10% flow reduction after 6 months of continuous operation when maintained properly.
Material Science and Performance Characteristics
Selecting appropriate filtration media requires understanding material properties beyond micron ratings. Stainless steel (316L grade) dominates high-temperature applications with service limits reaching 480°C, while polyester meshes offer chemical resistance to acids at pH levels below 3.0. Recent advancements in polypropylene blends have created meshes that resist chlorine degradation five times longer than standard polymers, extending functional lifespans. For biological applications, antimicrobial coatings reduce biofilm growth by 90% compared to untreated meshes. Critical mesh specifications include tensile strength (min 18N/mm²), open area percentage (optimal 28-35%), and controlled elongation rates below 2.5% at operating tensions.
Weaving Technology and Precision Production
Dutch twill weaving patterns create complex filtration structures with multiple overlapping wires, achieving micron ratings down to 5μm while maintaining flow rates impossible with simple weaves. Laser calibration during manufacturing maintains aperture tolerances within ±3μm across entire mesh sheets. For critical separation tasks, electroformed micro mesh delivers absolute filtration with pore uniformity at ±1μm. Modern production incorporates automated optical scanning detecting weaving defects at 120 frames per second, eliminating pinholes and inconsistent apertures that plagued early generation meshes.
Manufacturer Capability Comparison
| Producer |
Aperture Range (μm) |
Max Width (m) |
Materials Available |
Certifications |
Lead Time |
| Alpha Filtration |
5-2000 |
3.2 |
SS304/316, Monel, Bronze |
ISO 9001, ASME |
8 weeks |
| Beta Mesh Systems |
10-1500 |
2.4 |
Polyester, PP, Nylon |
FDA, USP Class VI |
4 weeks |
| Gamma Precision |
2-800 |
1.8 |
SS316L, Titanium, Inconel |
ISO 13485, PED |
10 weeks |
| Delta Filtertech |
15-3000 |
4.0 |
PVDF, PTFE-coated SS |
NSF/ANSI 61, WRAS |
6 weeks |
Industry-Specific Engineering Solutions
Effective filtration requires customized designs addressing distinct industry challenges. Beverage processors utilize self-cleaning mesh drums operating at 800L/m²/hour with integrated CIP systems maintaining hygiene standards. Municipal plants install stepped wedge wire screens with 1mm gaps handling raw sewage volumes exceeding 50,000m³/day while resisting fiber entanglement. For desalination pre-filtration, duplex woven meshes with nickel alloy reinforcement withstand saltwater corrosion for 15+ years. Semiconductor manufacturers require electrostatic-dissipative meshes maintaining surface resistance below 10⁹ ohms to prevent microchip damage. Such specialized solutions command 20-35% premiums over standard catalog items but deliver operational savings exceeding initial costs within 18 months.
Application-Based Performance Validation
A major bottled water producer replaced nylon mesh filters with 316 stainless steel units, reducing filter change frequency from biweekly to quarterly while increasing flow capacity by 28%. Pharmaceutical validation tests proved that multi-layer filtration meshes achieved LRV 7 reduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, meeting sterilization requirements. In Chinese textile dyeing facilities, custom calendered mesh belts withstand temperatures of 135°C while removing pigment agglomerates, extending service life from 3 months to 14 months. Offshore oil platforms utilize duplex 2205 stainless meshes for seawater intake screening, eliminating biological fouling that previously necessitated monthly cleaning cycles.
Evolution of Micro Mesh for Enhanced Filtration
Recent breakthroughs in nanotechnology enable ultrafine filtration capabilities previously unattainable. Electrospun nanofiber layers deposited on standard support meshes capture particles down to 0.1μm while maintaining flow rates comparable to conventional 10μm meshes. Smart mesh prototypes incorporate embedded conductivity sensors detecting pore blockages instantly by monitoring flow differentials across filter surface zones. Environmental developments include recyclable polymer meshes that decompose within 5 years instead of centuries. Research institutes report experimental graphene-coated meshes reducing hydraulic resistance by 75% compared to traditional materials. These innovations will redefine separation technology as global demand for precision filtration grows 8.7% annually through 2028.

(water filtration mesh)
FAQS on water filtration mesh
以下是根据您的需求创建的5组英文FAQs。每组问答围绕核心关键词"water filtration mesh"和相关词"filtration mesh"、"micro mesh for filtration"设计。问题使用HTML H3标签包裹(例如`
Q: ...
`),回答以"A: "开头,并确保问题和回答均控制在三句话内。整个内容以HTML富文本形式返回,使用`
`容器组织各个FAQ组。
Q: What is a water filtration mesh and how does it function?
A: Water filtration mesh is a porous netting material designed to remove impurities from water. It traps particles like sediment and debris as water flows through its micro-sized pores. This ensures cleaner water output for various purification systems.
Q: How is filtration mesh applied in everyday water systems?
A: Filtration mesh is commonly used in domestic filters, industrial processes, and agricultural irrigation. It screens contaminants such as dirt or sand during water flow. This application enhances the safety and clarity of filtered water efficiently.
Q: What types of micro mesh are available for advanced filtration?
A: Types include polyester, nylon, and stainless steel micro meshes with varying pore sizes. Each type caters to specific needs, like ultra-fine removal of microorganisms. These are ideal for high-precision applications in wastewater or desalination plants.
Q: What are the key benefits of using micro mesh for filtration?
A: Micro mesh offers excellent durability, resistance to clogging, and efficient particle capture. It can be reused multiple times and is eco-friendly compared to some filters. This provides cost-effective long-term performance in water treatment setups.
Q: How should I clean and maintain a water filtration mesh?
A: Rinse with clean water or gently brush to remove trapped debris. Avoid harsh chemicals to prevent material degradation. Regular maintenance prolongs the mesh's lifespan and ensures consistent filtration quality.
此HTML代码可直接复制到网页中使用,每个FAQ组结构清晰、简洁,且严格遵循三句话的限制。













![$item[title] $item[alt]](https://www.ccmetalmesh.com/images/cc-7691.webp)

